Embark on a journey into the realm of economics with the Production Possibilities Curve Practice Worksheet, an invaluable tool designed to empower you with a comprehensive understanding of this fundamental concept. This worksheet delves into the intricacies of PPCs, guiding you through their construction, shifts, and applications, equipping you with the knowledge and skills to analyze economic choices and compare economies.
As we navigate the complexities of production possibilities, we will explore the assumptions that underpin PPCs, unravel the factors that drive their shifts, and uncover the practical applications of this powerful tool. Join us as we unravel the secrets of economic decision-making, one curve at a time.
Introduction: Production Possibilities Curve Practice Worksheet
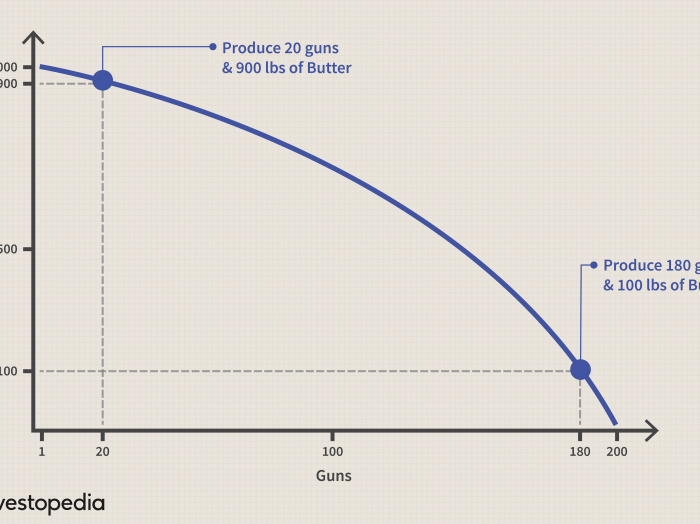
A production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the maximum possible combinations of two goods that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
The PPC assumes that the economy is operating at full employment, that resources are fully utilized, and that technology is fixed.
The PPC can be illustrated with a graph, with the production of one good on the horizontal axis and the production of the other good on the vertical axis. The curve itself represents the maximum possible combinations of the two goods that the economy can produce.
Shifting the PPC

The PPC can shift in response to changes in resources, technology, or the size of the labor force.
Resources
An increase in resources, such as land, labor, or capital, will shift the PPC outward, allowing the economy to produce more of both goods.
Technology, Production possibilities curve practice worksheet
An improvement in technology will also shift the PPC outward, as it allows the economy to produce more of both goods with the same resources.
Labor force
An increase in the size of the labor force will shift the PPC outward, as it allows the economy to produce more of both goods with the same resources.
Applications of the PPC
The PPC can be used to analyze economic choices and compare different economies.
Economic choices
The PPC can be used to illustrate the trade-offs that an economy must make when it produces different combinations of goods.
Comparing economies
The PPC can be used to compare the productive capacities of different economies. An economy with a larger PPC can produce more of both goods than an economy with a smaller PPC.
Limitations of the PPC
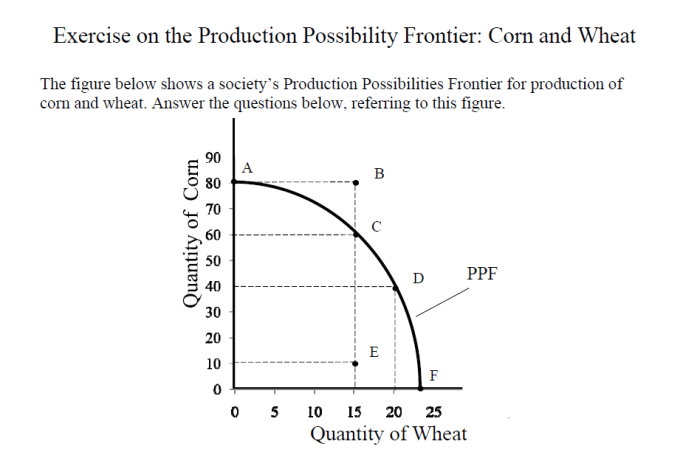
The PPC is a useful tool for analyzing economic choices, but it has some limitations.
- The PPC assumes that resources are fully utilized, which is not always the case in the real world.
- The PPC assumes that technology is fixed, which is not always the case in the real world.
- The PPC does not take into account the quality of goods, which can affect the overall productive capacity of an economy.
Practice Worksheet
The practice worksheet includes exercises on the following topics:
- Constructing PPCs
- Shifting PPCs
- Applying PPCs to economic analysis
Expert Answers
What is a production possibilities curve?
A production possibilities curve (PPC) is a graphical representation of the maximum combinations of two goods or services that an economy can produce with its given resources and technology.
What are the assumptions of a PPC?
The assumptions of a PPC include full employment of resources, fixed resources and technology, and constant opportunity cost.
How can I use a PPC to analyze economic choices?
A PPC can be used to analyze economic choices by identifying the opportunity cost of producing one good or service over another.