Ap physics 1 momentum and impulse frq – Delving into the realm of AP Physics 1: Momentum and Impulse, this exploration unveils the fundamental concepts, applications, and implications of these physical principles. Momentum and impulse, intertwined concepts that govern the motion of objects, hold immense significance in various scientific disciplines and everyday phenomena.
The following discourse provides a comprehensive examination of momentum and impulse, encompassing their definitions, relationships, and applications. Through real-world examples and problem-solving techniques, we delve into the practical implications of these concepts, unraveling their profound impact on our understanding of the physical world.
Momentum and Impulse Concepts
Momentum is a fundamental concept in physics that measures the quantity of motion of an object. It is defined as the product of an object’s mass and velocity. Impulse, on the other hand, is a force acting over a short period of time that can cause a change in momentum.
In real-world scenarios, momentum and impulse play a significant role in various phenomena, such as the motion of projectiles, collisions between objects, and the operation of rockets.
Examples of Momentum and Impulse
- A car has a large momentum due to its high mass and velocity.
- A baseball player experiences a large impulse when hitting a ball, causing the ball to change its momentum.
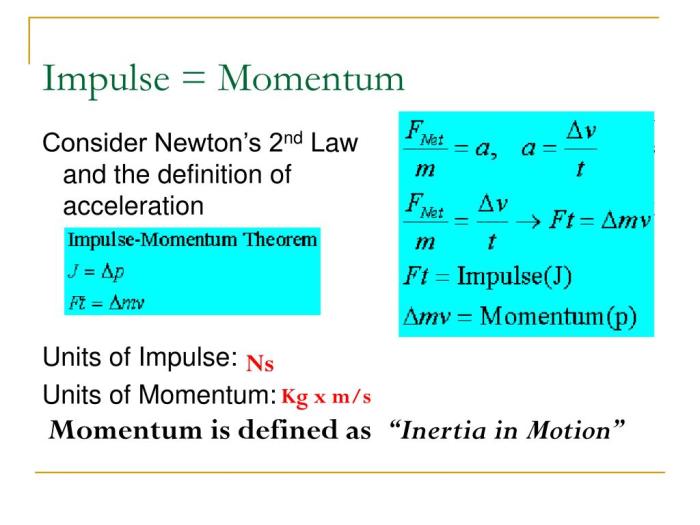
Impulse-Momentum Theorem
The impulse-momentum theorem is a fundamental law of physics that states that the impulse applied to an object is equal to the change in its momentum. This theorem is expressed mathematically as:
Impulse = Final Momentum- Initial Momentum
This theorem is significant because it allows us to calculate the change in momentum of an object when the impulse acting on it is known.
To apply the impulse-momentum theorem, we need to know the initial and final velocities of the object, as well as the time over which the impulse is applied. Once we have this information, we can use the following steps to solve problems involving momentum and impulse:
- Calculate the impulse by multiplying the force by the time over which it is applied.
- Calculate the change in momentum by subtracting the initial momentum from the final momentum.
- Set the impulse equal to the change in momentum.
- Solve for the unknown variable (usually the velocity or time).
Conservation of Momentum, Ap physics 1 momentum and impulse frq
The principle of conservation of momentum states that the total momentum of a closed system remains constant. This principle is based on the fact that momentum cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred between objects. Conservation of momentum is applied in various physical situations, such as:
- Collisions between objects
- Rocket propulsion
- Fluid dynamics
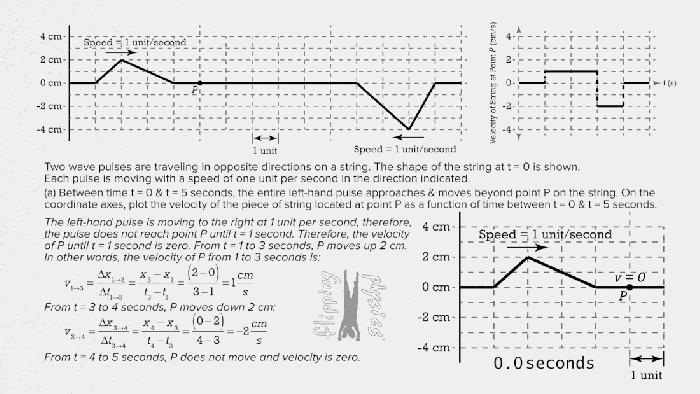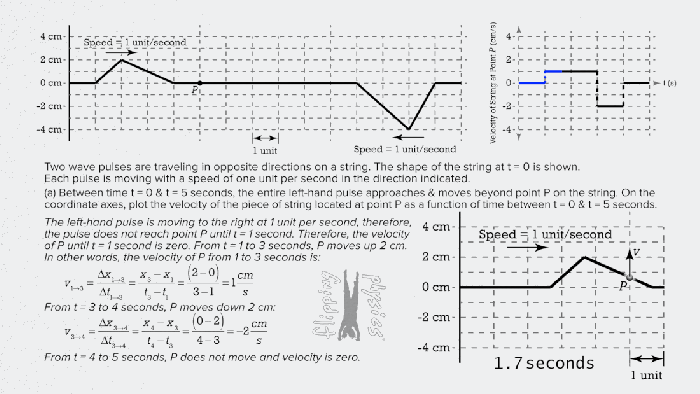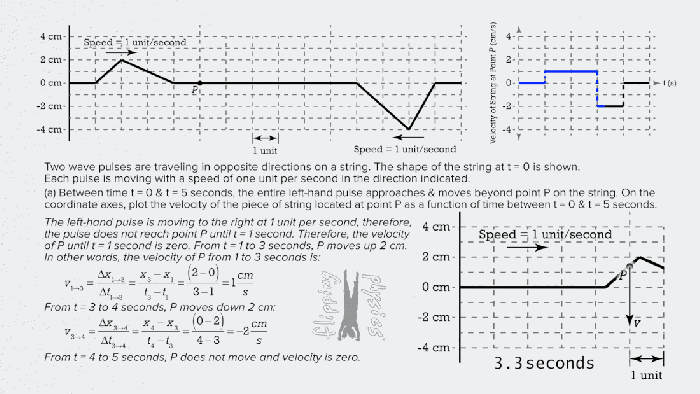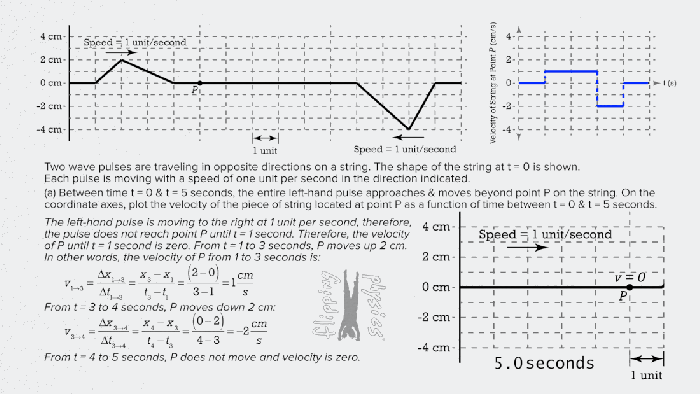
Collisions in One Dimension
Collisions can be classified into three types based on the amount of kinetic energy lost during the collision:
- Elastic collisions:No kinetic energy is lost during the collision.
- Inelastic collisions:Some kinetic energy is lost during the collision.
- Perfectly inelastic collisions:All kinetic energy is lost during the collision.
To analyze collisions using the conservation of momentum principle, we need to know the masses and velocities of the objects involved in the collision. We can then use the following steps:
- Calculate the total momentum of the system before the collision.
- Calculate the total momentum of the system after the collision.
- Set the total momentum before the collision equal to the total momentum after the collision.
- Solve for the unknown variables (usually the velocities after the collision).
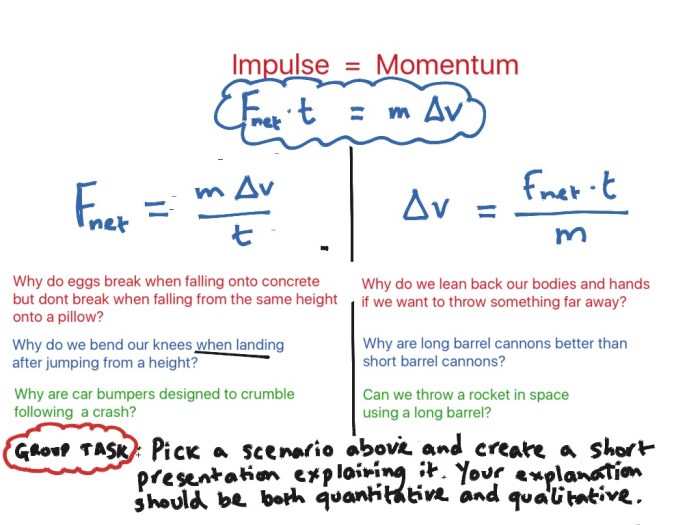
Applications of Momentum and Impulse
Momentum and impulse have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Sports:Calculating the momentum of a baseball or football can help determine the distance it will travel.
- Engineering:Designing safety features in vehicles to minimize the impact of collisions.
- Medicine:Measuring the impulse applied to the body during a fall or impact can help assess the severity of injuries.
Detailed FAQs: Ap Physics 1 Momentum And Impulse Frq
What is the impulse-momentum theorem?
The impulse-momentum theorem states that the net impulse acting on an object is equal to the change in its momentum.
How is the principle of conservation of momentum applied in real-world situations?
The principle of conservation of momentum is applied in various situations, such as analyzing collisions, rocket propulsion, and the motion of fluids.
What are the different types of collisions?
There are three main types of collisions: elastic, inelastic, and perfectly inelastic.