One of these attribution models distributes the credit evenly across all touchpoints, providing a comprehensive view of marketing campaign performance. This model, known as the linear attribution model, assigns equal weight to each touchpoint, recognizing the cumulative impact of marketing efforts on customer conversions.
The linear attribution model offers a balanced approach, acknowledging the contributions of all touchpoints in the customer journey. It is particularly useful when multiple touchpoints are involved and their individual impact is difficult to isolate. By distributing the credit evenly, this model provides a holistic understanding of campaign effectiveness and helps businesses optimize their marketing strategies.
Attribution Models

Attribution models are frameworks that help marketers understand the impact of different marketing touchpoints on customer conversions. By assigning credit to each touchpoint, attribution models enable businesses to evaluate the effectiveness of their marketing campaigns and optimize their marketing spend.
There are various types of attribution models, each with its own unique approach to distributing credit. The choice of attribution model depends on the specific business objectives, marketing strategies, and data availability.
One of These Attribution Models Distributes the Credit
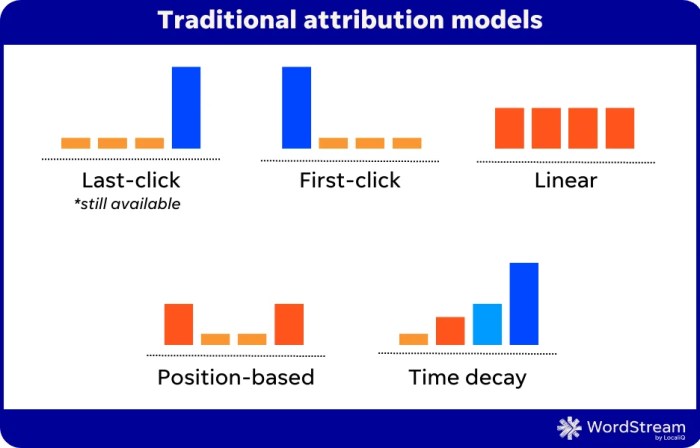
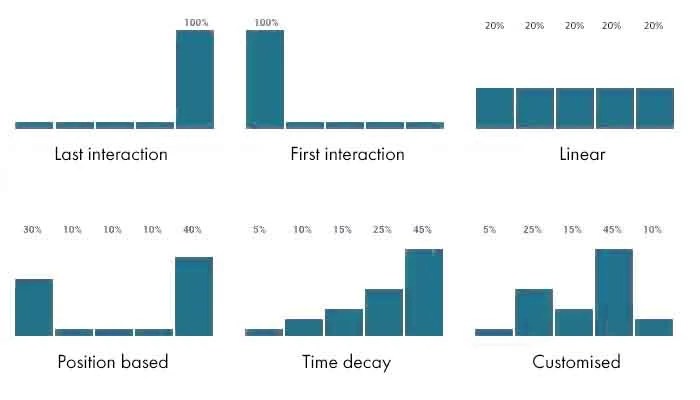
One of the commonly used attribution models is the linear attribution model. This model distributes the credit evenly across all touchpoints involved in the customer journey.
The linear attribution model assumes that each touchpoint plays an equally important role in influencing the customer’s decision-making process. It assigns the same weight to all touchpoints, regardless of their position or timing in the customer journey.
For example, if a customer interacts with an email campaign, visits a website, and makes a purchase after seeing a social media ad, the linear attribution model would attribute 25% of the credit to each of these touchpoints.
Advantages of the Linear Attribution Model:
- Simplicity: Easy to understand and implement.
- Fairness: Distributes credit evenly, avoiding bias towards any specific touchpoint.
- Comprehensive: Captures the impact of all touchpoints involved in the customer journey.
Disadvantages of the Linear Attribution Model:
- Oversimplification: May not accurately reflect the varying influence of different touchpoints.
- Less actionable insights: Does not provide detailed information about the most effective touchpoints.
Comparison with Other Attribution Models
| Attribution Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-touch | Attributes all credit to the first touchpoint in the customer journey. | Simple and easy to implement. Gives credit to the initial touchpoint that sparked interest. | Overvalues the role of early touchpoints. Ignores the impact of subsequent touchpoints. |
| Last-touch | Attributes all credit to the last touchpoint in the customer journey. | Easy to implement. Gives credit to the touchpoint that directly led to conversion. | Overvalues the role of late touchpoints. Ignores the impact of earlier touchpoints. |
| Position-based | Distributes credit based on the position of touchpoints in the customer journey. | Provides more nuanced insights than first-touch or last-touch models. Gives credit to touchpoints that occur at key stages of the journey. | Complex to implement. May require additional data and analysis. |
Considerations for Choosing an Attribution Model
When choosing an attribution model, businesses should consider the following factors:
- Marketing objectives: Different attribution models align with different marketing goals. For example, the first-touch model is suitable for lead generation campaigns, while the last-touch model is more appropriate for direct sales campaigns.
- Customer journey: The complexity and length of the customer journey influence the choice of attribution model. Position-based models are more suitable for complex customer journeys with multiple touchpoints.
- Data availability: The availability and quality of data impact the choice of attribution model. Some models, such as position-based models, require detailed data on customer interactions.
Applications and Use Cases
Businesses have successfully implemented the linear attribution model in various marketing campaigns. For example, an e-commerce company used the linear attribution model to evaluate the effectiveness of its email marketing, social media advertising, and search engine optimization () efforts.
The linear attribution model helped the company understand the impact of each touchpoint on customer purchases. By analyzing the data, the company identified that email marketing played a significant role in generating leads, while social media advertising and contributed to conversions.
Based on these insights, the company optimized its marketing spend by increasing its investment in email marketing and . This resulted in a significant increase in sales and improved return on investment (ROI).
Future Trends and Developments
Emerging trends in attribution modeling include:
- Multi-touch attribution: Models that consider the combined impact of multiple touchpoints on conversions.
- Machine learning and AI: Algorithms that analyze large datasets to identify patterns and optimize attribution.
- Cross-channel attribution: Models that track customer interactions across multiple channels and devices.
These advancements will enable businesses to gain deeper insights into the customer journey and optimize their marketing campaigns more effectively.
FAQ Explained: One Of These Attribution Models Distributes The Credit
What is the key difference between the linear attribution model and other models?
The linear attribution model distributes credit evenly across all touchpoints, while other models, such as first-touch or last-touch, assign credit to specific touchpoints based on their position in the customer journey.
When is the linear attribution model most appropriate?
The linear attribution model is most appropriate when multiple touchpoints are involved and their individual impact is difficult to isolate, such as in complex marketing campaigns or long customer journeys.
How can businesses use the linear attribution model to improve their marketing strategies?
By distributing the credit across all touchpoints, the linear attribution model provides a holistic understanding of campaign effectiveness. This information can help businesses identify areas for improvement, optimize their marketing mix, and allocate resources more effectively.